C# 14 Extension Members: Cleaner Code
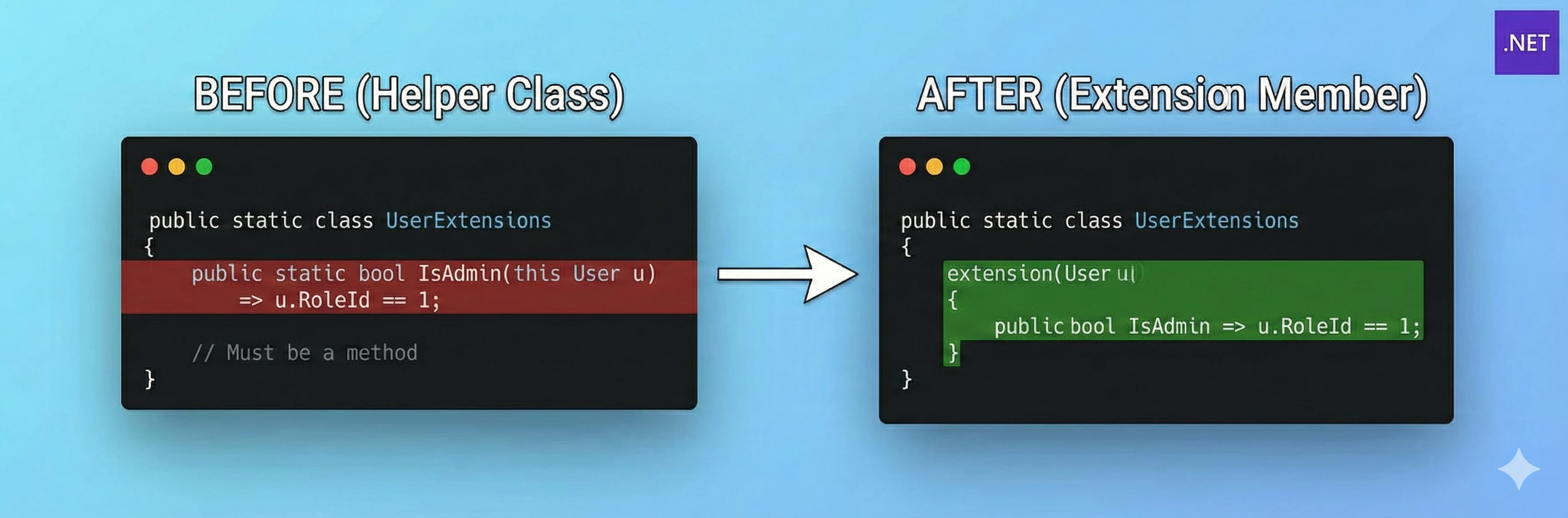
The era of the ‘Helper Class’ is over. C# 14 introduces Extension Members, allowing you to add properties, operators, and static methods to external types. Here is how to modernize your codebase.

The era of the ‘Helper Class’ is over. C# 14 introduces Extension Members, allowing you to add properties, operators, and static methods to external types. Here is how to modernize your codebase.
Real benchmark results comparing IAsyncEnumerable and Task.WhenAll. Learn when to choose speed vs responsiveness, memory efficiency, and user experience in C# async operations.
Most projects I review have a Utils or Helpers class packed with static methods. At first glance, static helpers look like the fastest way to solve problems. You don’t need to new up objects or wire dependencies. Just call Helper.DoSomething() and move on. That convenience is exactly why they sneak into codebases. But over time, static helpers turn into a source of pain, especially in production systems that need to evolve. ...
Async/await is powerful but overused. This guide breaks down async misconceptions, shows real enterprise use cases, and gives you a practical decision framework for async in C#.
Learn why preferring interfaces over abstract classes in C# improves code flexibility, testability, and maintainability for robust .NET applications.
Master IEquatable in C# to optimize equality checks, improve collection performance, and eliminate boxing overhead. Essential for value types and collections.
A practical guide to C# Default Interface Methods: how to use them, when to avoid them, and how they help you build future-proof APIs.
Discover the best practices for encapsulation in C#. Learn when to use auto-properties, when to switch to backing fields, and how to keep your property setters clean, focused, and maintainable with practical examples and actionable guidelines.
Discover why structs as dictionary keys can cause hidden allocations in C#. Learn how to implement IEquatable, use readonly and record structs, and write allocation-free, high-performance code for hot paths.
Discover how guard clauses in C# simplify validation and error handling. Learn to write fail-fast code, avoid nested conditionals, and keep business logic clean with modern language features and reusable helpers.