Delete-Driven Design: How to Write Code You Can Remove
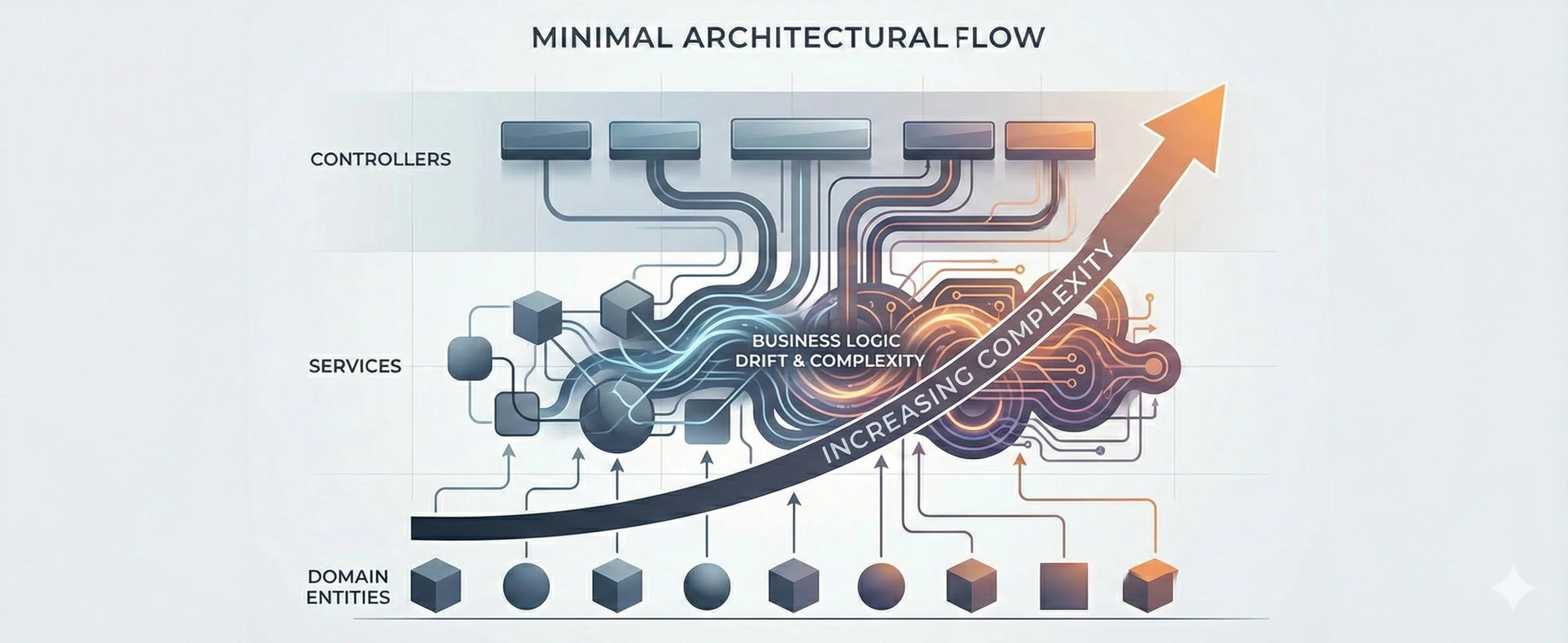
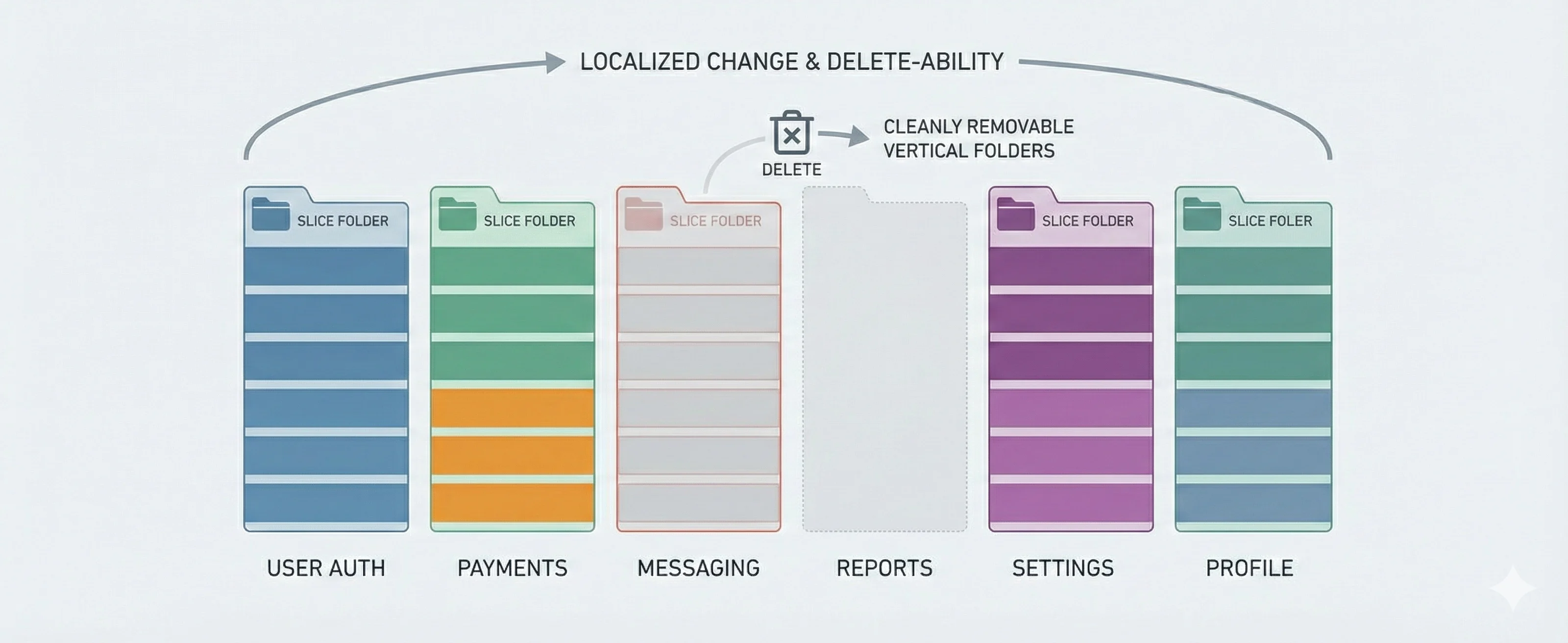
Most design principles focus on extensibility and reuse. Delete-Driven Design flips the question: how easy is it to remove code safely? This post explains why delete-ability is the ultimate test of boundaries, abstractions, and tests—and how to design systems that accept change without fear.